A Practical Guide to GA4 Event Parameters for Marketers

Using GA4 effectively will help answer two key questions.
- Does my work have a result?
- Is my work having any noticeable impact on our client’s business?
Compared to Universal Analytics, Google Analytics 4 uses a new event-driven model. This offers analysts and website owners more ways to analyze user behavior or attribute conversions on a client’s website in real time.
You don’t need to be an expert in GA4. However, understanding how events and event parameters work in GA4 will help you answer these two questions confidently. You’ll be able to create custom reports and provide more valuable advice for your clients—whether you’re updating them on SEO progress or reporting on paid advertising campaigns.
This beginner's guide will help if you're confused or need a quick review of GA4’s parameters. It covers the basics of GA4 parameters and shows you how to use them in client reports.
Table of contents
- DashThis Explains: What are events in GA4 and why are they useful?
- What are the different types of events in GA4?
- Event parameters in GA4 explained
- A step-by-step tutorial on using GA4 events in your data tracking
- How to integrate GA4 event data with DashThis
- Automate your GA4 reporting with DashThis
DashThis Explains: What are events in GA4 and why are they useful?
First, let’s understand what events are in GA4.
Events are actions visitors take on your website or app, which can be:
- Viewing an about me page
- Filling out a contact form
- Scrolling down a page to read a blog post or interact with a landing page.
All GA4 events have a name and parameters, which update a dimension or metric in Google Analytics reports.

Source: Google
Here, the event ad_click describes the action, while the parameter ad_event shows the unique ID of the event triggered for closer analysis.
GA4 automatically collects event data as visitors interact with a website by default. However, you don’t need to collect and track everything—only the interactions crucial to your client’s business. Instead, focus your tracking on events tied to your business goals and mark them as key events (formerly known as conversions).
For example, suppose your lead generation typically relies on form submissions and phone calls. You'll define these interactions as key events for closer tracking.
What are the different types of events in GA4?
Different GA4 event types use different data collection approaches.
Automatically collected events:
GA4 automatically collects these events. No setup needed.
Enhanced measurement events:
GA4 can collect this data once you’ve enabled enhanced measurement.
Recommended events:
Google recommends tracking these events for more meaningful reports. Depending on your data analysis goals, you’ll need to set these up and configure them in GA4.
Custom events
Google does not automatically track these. You must implement these custom events using tools like Google Tag Manager or manually through a developer.
Common GA4 events to start your tracking journey
These events help track common user interactions on your website.
- Page view (event name:page_view) How often someone loads and views a page
- Scroll depth: (event name:scroll_depth) Shows how far users scroll down your page. GA4 triggers the event by default when a user scrolls through approximately 90% of the page. You can change this threshold with custom scroll tracking events in Google Tag Manager.
- Click: (event name: click) This click event measures page clicks or interactions on a specific call-to-action button, such as an add-to-cart or an outbound link. It can help you identify which CTA buttons are converting more users.
- Video progress (event name: video_progress) Tracks video watch time by measuring the amount of video a user watches on your website.
- Measure file download: (event name: file_download) Records the number of file downloads, helping you assess the performance of a landing page with a content offer.
- Form submission: (event name: form_submission) Tracks how often users click a form submission button. This event helps you understand how your marketing campaigns influence user interactions.
- Purchases (event name: purchase) If you sell products on a website, this event tracks purchasing behavior.
- View site search results (event name: view_search_results): This event helps you understand how users interact with search results on your website, including which search terms they use. Note that you’ll need enhanced measurement to track search behavior.
Event parameters in GA4 explained
If events describe interactions, event parameters provide additional information on these actions. This parameter data also populates dimensions and metric reports in GA4 for segmentation, comparison across different groups, or KPI tracking.
For instance, suppose you’re monitoring the number of purchases made by an e-commerce store over the last three months. You can use parameters to create custom dimensions and GA4 metrics that detail the purchased product, such as its name, category, and price. These attributes can be beneficial when segmenting your data for analysis.
Here’s how event parameters might help an e-commerce store owner analyze their website data more effectively.
- order_total: Tracks the total value of each order.
- product_ids: Tracks the products purchased in a transaction. Useful to identify complementary products, or uncover upselling or cross-selling opportunities.
- coupon_code: Tracks which coupon codes your customers use - especially if you want to know the effectiveness of a sale or promotion
Event parameter types in GA4
There are two types of event parameters in GA4: automatically collected and custom.
Automatically collected parameters
GA4 automatically collects some event parameters for you to use as a starting point for your reporting. Some examples include:
- Content_group: The content group associated with a page or screen.
- Content_id: The unique ID of a piece of content a user interacted with. Useful to understand which content pieces on your website contributed to a specific user journey
- Page_location: Page URL of the page that someone visited on your website.
- Page_referrer: Which URL referred a user to your website
- Page_title: The page title of a webpage
View Google’s full drop-down list of event parameters and list of automatically collected event parameters for more information.
Custom event parameters and how to set them up in GA4
Custom event parameters help you capture more relevant data for your business. You’ll need to set these up manually in Google Tag Manager or GA4.
Take note of these GA4 event naming rules
- Start event names with a letter, not a number or symbol
- Only use letters, numbers and underscores when naming events. Don’t use hyphens or spaces.
- Consider that event names are case-sensitive. Form_link_click and form_link_click are two distinct events.
- Avoid using reserved event names like page_view, video_start, first_visit, scroll, click, file_download already tracked by GA4. These apply to events tracked automatically or under enhanced measurement.
- Keep event names and parameter values under 40 characters
Check out Google’s step-by-step guide on creating event parameters in GA4.
A step-by-step tutorial on using GA4 events in your data tracking
Step 1: Plan your event tracking strategy
Before you implement your event tracking in GA4, take a step back to create a tracking plan. Review your client’s business goals and which interactions align with these business goals. These steps ensure you only track the data that matters most to your clients.
- Define your business goals: These can include conversion, sales, retention, or engagement goals. Ideally, every tracked event aligns with a business goal.
- Identify valuable user actions: For e-commerce, these can be adding items to a cart, whereas for SaaS platforms, these can be filling in a form for a free trial or interacting with a product demo video. You can also track micro-conversions, that are steps leading up to a conversion event, such as downloading a content offer or visiting a product page.
Step 2: Use meaningful and consistent event naming conventions
Keep your GA4 event naming structure consistent. It should also be simple enough to identify an event’s purpose from a glance.
What does this work in practice? Anton Kovalchuk, Founder and CEO of QliqQliq, says consistency and documentation help keep different teams aligned and minimize confusion during data analysis.
“ For structuring event names, consistency is critical. We follow a standardized naming convention that keeps event names descriptive yet concise. For example, we use a "category_action_label" structure, such as "button_click_download" or "form_submit_contact." This makes it easier to analyze reports later without confusion.
Likewise, David Hunter of Local Falcon says: “I keep it simple, using lowercase and underscores to maintain consistency. Generic event names like “click” or “interaction” are useless without context. Instead, I prefer a structure like “form_submit” or “video_watch” with parameters specifying which form or video.”
Once you’ve created an event naming convention, document it in a shared document. Share this with everyone involved, especially marketers, developers, and data analysts,, to help you organize and align your event tracking efforts. Crystal Widjaja, writing for Reforge, provides a handy event tracking template to use for reference.
Step 3: Identify relevant event parameters
Event parameters can help capture relevant data around an event. Besides the default parameters already captured by GA4, consider whether you need to define event parameters for more specific insights pertinent to your client’s goals.
“For instance, if we are tracking form submissions for lead capture, then we might include form_type, user_role, or campaign_source to get even more granular insights. The advantage of using these custom parameters is that we can segment in much more detail in the reports of GA4 and remarket more precisely on Google Ads.
Anton Kovalchuk, Founder and CEO at QliqQliq.com
Step 4: Implement custom event tracking using Google Tag Manager (GTM)
Now that you have defined your events and parameters, it's time to add them to your website. There are three ways to install these custom events.
- Use Google Tag Manager
- Create them in GA4 under Admin > Data display > Events > Create event
- Manually add them to your client’s website with developer support
We recommend using Google Tag Manager, as it’s the most flexible solution. It helps you configure, deploy, and update event tracking quickly without developer support. Google Tag Manager also provides a centralized platform for managing all your tracking codes, making it easier to share information with team members or test whether events are firing properly.
Use these steps to set up Google Analytics event tracking in Google Tag Manager.
Step 5: Test and validate event tracking
Before launching, test to ensure you’ve set everything up correctly. Use tools like GA4’s DebugView and GTM’s preview mode to validate whether events are firing correctly and whether the numbers in GA4 and other tools, such as your CRM or other platforms, match up. Adjust your tracking as needed.
How to integrate GA4 event data with DashThis
GA4 provides a lot of data for analyzing website performance. But how do you make sense of all that data or sift out what applies to your client’s business without overwhelming your client or ensuring that the data is accurate and trustworthy?
Report automation tools like DashThis can help visualize and analyze your GA4 event data to help you explore your website data more effectively. You can also combine website data with marketing data to provide an overview of your client’s marketing efforts in one dashboard.
How to set up a GA4 dashboard in DashThis
First, let’s create your GA4 dashboard template in DashThis.
Follow these steps once you’ve signed up for DashThis’s 15-day trial.
- Click +New Dashboard
- Choose one of our reporting templates (we’ll use the GA4 reporting template in this walkthrough)
- Name it and click Next
Add your GA4 account and property as a data source to DashThis. Then, add the events and parameters you want to analyze and report using our drag-and-drop builder.
You can also use DashThis’s widget bundles to add relevant data to your reports quickly. So, if you’re reporting on e-commerce revenue and conversions, there’s a widget bundle that allows you to add all the related metrics with a click.
DashThis’s GA4 report template
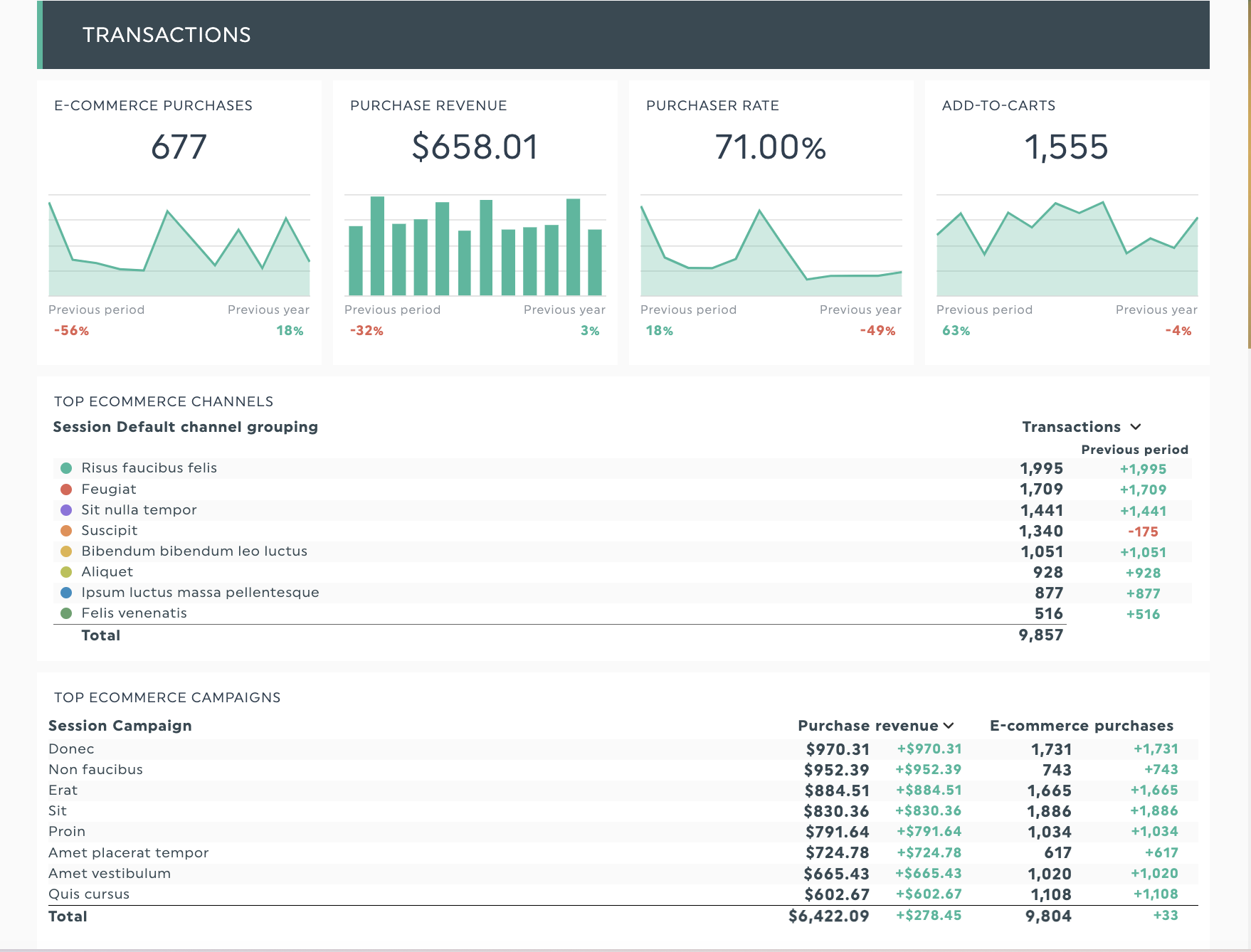
Get this GA4 report template with your own data!
Make sense of your GA4 reporting with DashThis’s report template.
Features of this report template:
- Analyze user events like page views, total visits, page views, and engaged sessions by source to show you which channels people interact with to find your app or website
- Get a quick overview of key events for the month like purchase rate, add-to-cart, or checkout completions
- To track which marketing campaign brings in the best ROI, break down marketing campaign effectiveness by the number of purchases and purchase revenue.
3 ways to use GA4 event insights in DashThis for your marketing reporting
Get an overview of key event metrics and trends
Conversions are now key events in GA4. Reserve these key events for business interactions that lead directly to a sale or put users further down the sales customer journey. For example, an e-commerce store optimizing its checkout process could track key events to search queries, product add-to-carts, or checkout opens for more actionable data. You’ll know which actions to take and advise your client accordingly.
Compare event performance across different segments and dimensions.
Aggregated data is excellent for a broad overview, but you’ll need to dive deeper to analyze data further. Using GA4, you can compare engagement metrics across different data segments or custom definitions you’ve previously created. For example, let’s say you’re trying to identify your most profitable product categories for an e-commerce client. Using GA4, you can compare event performance, like conversions and click-through rates, to get a better understanding.
You can also analyze event engagement over the week to identify ideal social media posting times and the click-through rate across social media channels to determine which channel drives the most engaged viewers. It all depends on your client’s business goals and your analytical aims.
Share event insights with stakeholders through automated reporting
Besides an easy-to-use interface, one part often overlooked is getting the report to your clients and internal stakeholders. DashThis offers a variety of report automation and scheduling options to simplify this process, including:
- Automated email dispatch and scheduling
- PDF downloads for offline viewing
- URL sharing
Automate your GA4 reporting with DashThis
Tracking GA4 events and understanding event parameters not only help you understand and analyze data more effectively. By You’ll find more ways to communicate the value of your work to your clients.
GA4 provides a robust framework for tracking user interactions. Combine GA4 events with your marketing data in DashThis to get a complete view of your marketing efforts.
Ready to automate your GA4 reporting?
Read More
Don’t miss out!
Automate your reports!
Bring all your marketing data into one automated report.
Try dashthis for free
